 Solar power is generated through the use of photovoltaic (PV) systems, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how solar power is generated:
Solar power is generated through the use of photovoltaic (PV) systems, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how solar power is generated:
- Sunlight: Solar power generation starts with sunlight. Photons, which are particles of light, are emitted by the Sun and travel through space to reach the Earth.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, also known as solar modules or photovoltaic panels, are made up of multiple solar cells. These panels are typically installed on rooftops or in open areas where they can receive maximum sunlight exposure. The solar cells within the panels are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which can absorb photons.
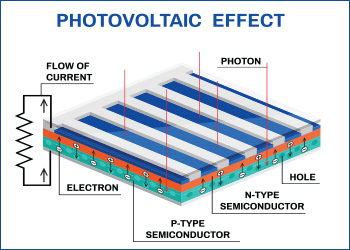
- Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight strikes the solar cells, the photons transfer their energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material. This causes the electrons to become energized and break free from their atomic bonds, creating a flow of electricity. This phenomenon is known as the photovoltaic effect.
- DC Electricity: The liberated electrons flow through the semiconductor material in a single direction, creating a direct current (DC) of electricity. However, DC electricity is not suitable for most household and commercial applications.
- Inverter: To convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses, an inverter is employed. The inverter takes the DC electricity and converts it into AC electricity.
- Electrical Grid Connection: The AC electricity produced by the inverter is then sent to the electrical panel of the building, where it can be used to power appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices. Any excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be fed back into the electrical grid, often through a process known as net metering, where the utility company credits the owner for the excess power.
- Monitoring and Control: Solar power systems often include monitoring and control mechanisms that allow the owners to track the performance of the system, measure the amount of electricity generated, and identify any issues or inefficiencies.
It’s worth noting that solar power generation can also be achieved through concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, which use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, typically a fluid-filled pipe or a tower, to produce heat. This heat is then used to generate electricity through conventional steam turbines. However, the majority of residential and commercial solar installations rely on PV systems.
For more information on solar visit our other blogs on How Solar Energy Works Everywhere and How Solar Energy Reduces Pollution. Click these links to learn more about our Residential Solar Solutions or Commercial and Industrial Solar Solutions at MB HAYNES.
